Wi-Fi WAN
Introduction
In an era where reliable internet access is essential, utilizing a Wi-Fi WAN (Wi-Fi Wide Area Network) connection offers a flexible solution for various scenarios. This approach allows users to connect to the internet wirelessly, making it particularly useful in locations where wired connections are unavailable or impractical. This document outlines the steps to effectively set up Wi-Fi WAN, detailing the necessary equipment, configuration steps, and verification methods.
Please note that this example is based on specific prerequisites and topology. D-Link does not guarantee compatibility with all platforms or clients.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with the configuration, ensure that you have the following prerequisites.
1. An M2M device with a Wi-Fi feature
2. At least one device:
- A PC, laptop, or tablet is required to configure the M2M device.
- This feature is applicable to the following models:
DWM-313, DWM-530-T, DWM-550-G, DOM-550-GSO, DTM-550-G
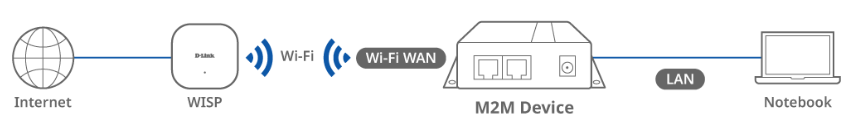
Topology
In this topology, the M2M device is the central component that enables the Wi-Fi WAN functionality. The laptop computer can connect to the Internet through the M2M device, achieving wireless Internet access.
Note: Before starting this configuration, please make sure the basic network settings of the D-Link M2M device are configured properly.
Configuration
Configuring a Wi-Fi WAN involves several key steps. Each step is crucial to ensure proper connectivity and functionality. Below are the detailed steps:
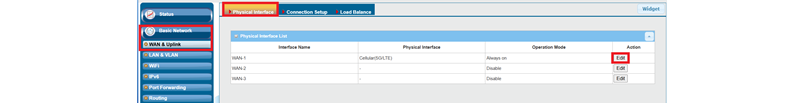
1. Physical Interface Configuration:
Go to Basic Network > WAN & Uplink > Physical Interface tab
The Physical Interface allows users to set up the physical WAN interface and adjust the WAN’s behavior, as shown below.
When the Edit button is applied, an Interface Configuration screen will appear. WAN-1 interface is used in this example. Select Wi-Fi Module One > Save tab
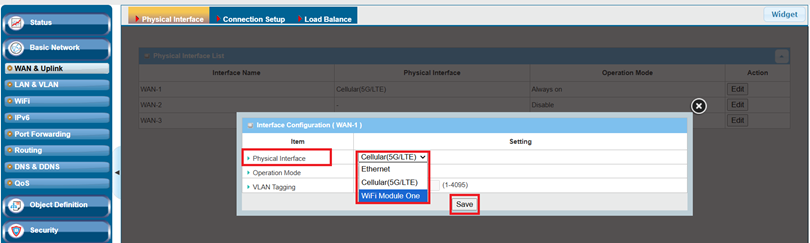
| Item | Descrption |
|---|---|
| Physical Interface |
Select Wi-Fi Module one |
| Operation Mode | Select Always on to make this WAN always active |
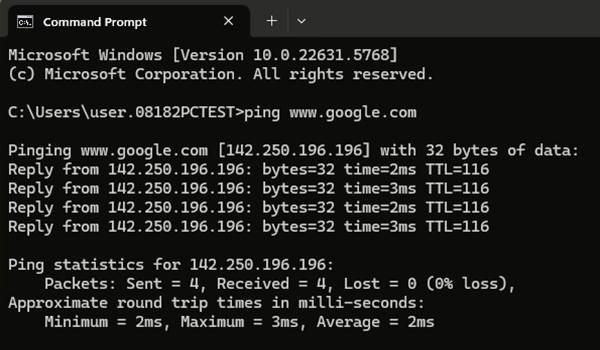
Test Result
A laptop connected via Ethernet to the M2M device, which accessed the Internet through a Wi-Fi WAN connection. Stable connectivity was verified by running ping www.google.com in Windows Command Prompt (cmd.exe).