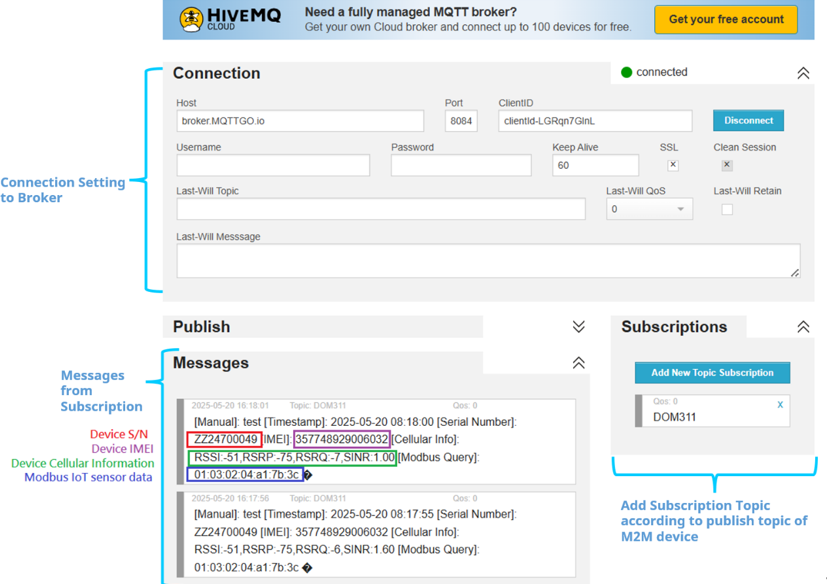
Sending Messages to the MQTT Broker
Introduction
MQTT is a messaging protocol based on the publisher/subscriber paradigm. A broker can be seen as a bridge for data transmission. In this example, we will demonstrate the MQTT configuration of an M2M DOM series device based on an RS-485 IoT sensor and transmit data via topic.
Prerequisites
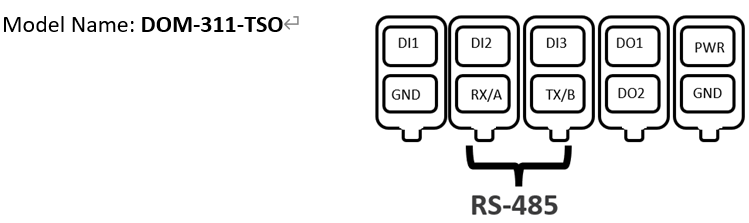
1. M2M Device and IoT Sensor (Temp/Humidity) Sides:
Use A and B to connect DOM series products based on IoT sensors (temperature/humidity).
This feature is applicable to the following models:
2. MQTT Broker and Subscriber:
In this example, we use HIVEMQ as the subscriber and MQTTGO as the broker as shown below. Furthermore, we use the same topic for both the M2M device publisher and the subscriber.
1. MQTT Broker (MQTTGO):
Address: broker.MQTTGO.io
Port: 1883
WSS Port: 8084
2. Subscriber (HIVEMQ):
https://www.hivemq.com/demos/websocket-client
Note: MQTT Broker and Subscriber are selected by you. D-Link cannot guarantee compatible functionality.
Topology
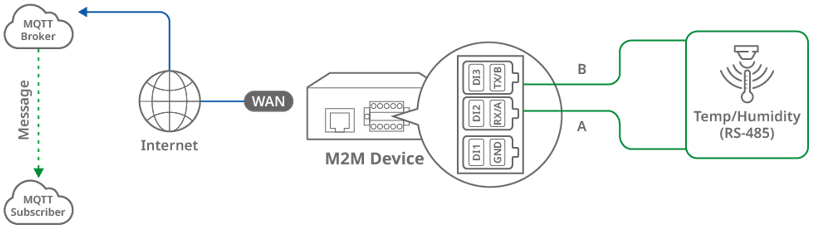
For example, we use the DOM-311-TSO, broker MQTTGO, and Subscriber HIVEMQ. The D-Link DOM-311-TSO device on the left has an RS-485 interface to connect A and B to the IoT sensor.
The DOM-311-TSO reads IoT sensor data and 4G-related information through the Modbus RTU protocol, then publishes topic A (including messages) and forwards topic A to broker. Subscriber HIVEMQ subscribes to topic A, whose messages include temperature, humidity and 4G-related information, and continues to collect topic A from the broker.
Note: Before starting MQTT configuration, please make sure the basic network settings of the D-Link M2M device are configured properly.
Configuration
1. RS-485 Port Configuration:
Go to Setup > Bus & Protocol > Port Configuration tab
Please set the RS-485 baud rate according to the IoT sensor specification.
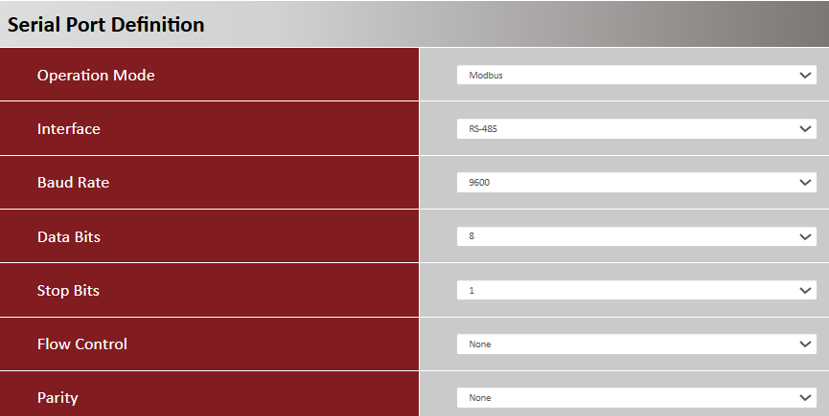
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Operation Mode | Displays the Modbus mode |
| Interface | Select the RS-485 physical interface for connecting to the access device(s) with the same interface specification |
| Baud Rate |
Select the appropriate baud rate for serial device communication RS-485 can use higher baud rate for 9600. Baud rate depends on the cable length and the installed environment, the longer the cable, the lower the baud rate. |
| Data Bits | Select 8 or 7 for data bits |
| Stop Bits | Select 1 or 2 for stop bits |
| Flow Control |
Select None / RTS, CTS / DTR, DSR for Flow Control in RS-232 mode Flow Control support depends on the model purchased |
| Parity | Select None / Even / Odd for Parity bit |
| Save | Click the Save button to save settings |
2. Modbus configuration:
Go to Field Communication > Bus & Protocol > Modbus tab
Please set the Listen Port and Slave mode according to the IoT sensor specification.
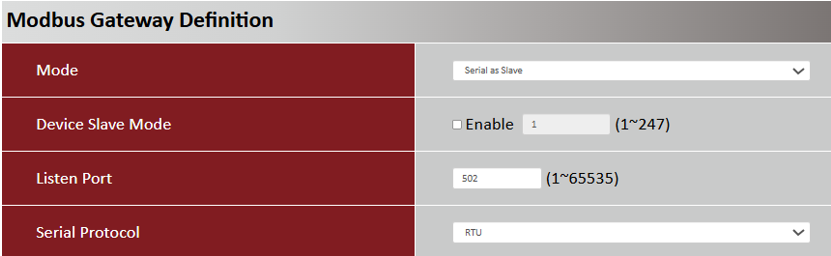
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Mode | Serial as Slave: Select this when the attached serial device(s) are all Modbus Slave devices |
| Device Slave Mode | Disable. The M2M device does not require slave-mode data checking. |
| Listen Port |
Use 502 port for the listen port Value Range: 1 - 65535 |
| Serial Protocol | Select the serial protocol RTU that is adopted by the attached Modbus device(s) |
3. MQTT configuration:
Go to Advance > Data to Server > MQTT tab
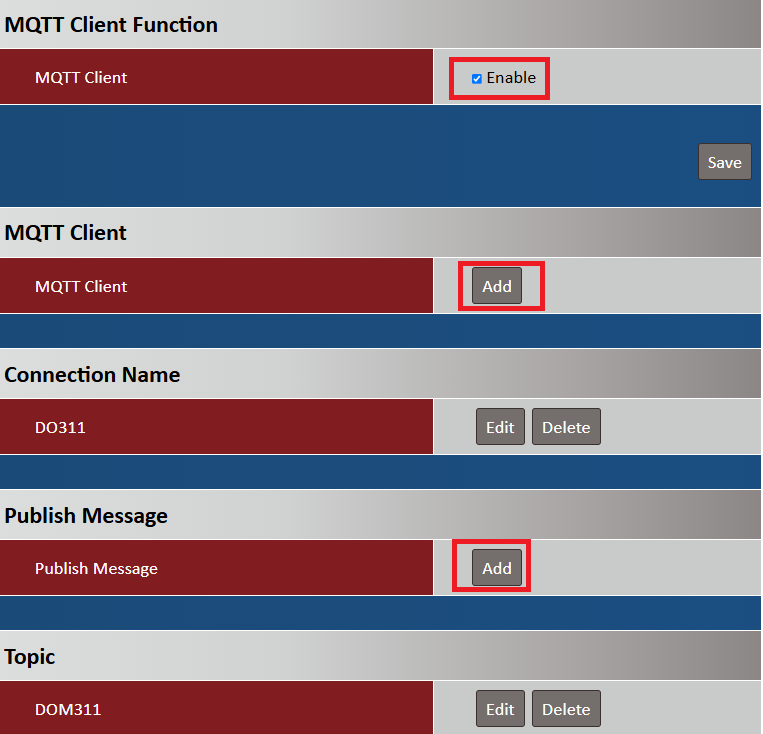
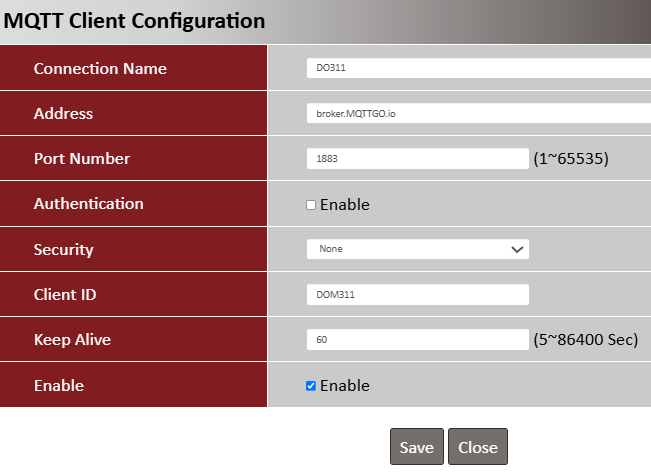
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | Specify a name as the identifier of the MQTT client |
| Address | Specify the host name or IP address of the MQTT broker that the client is going to publish messages to |
| Port Number |
Specify a port as the port for MQTT connection Value Range: 1 - 65535 |
| Authentication | Uncheck |
| Security | None |
| Client ID | Specify a unique ID for the MQTT client |
| Keep Alive | Specify a Keep Alive interval to keep the connection alive while the connection is idle |
| Enable | Enable |
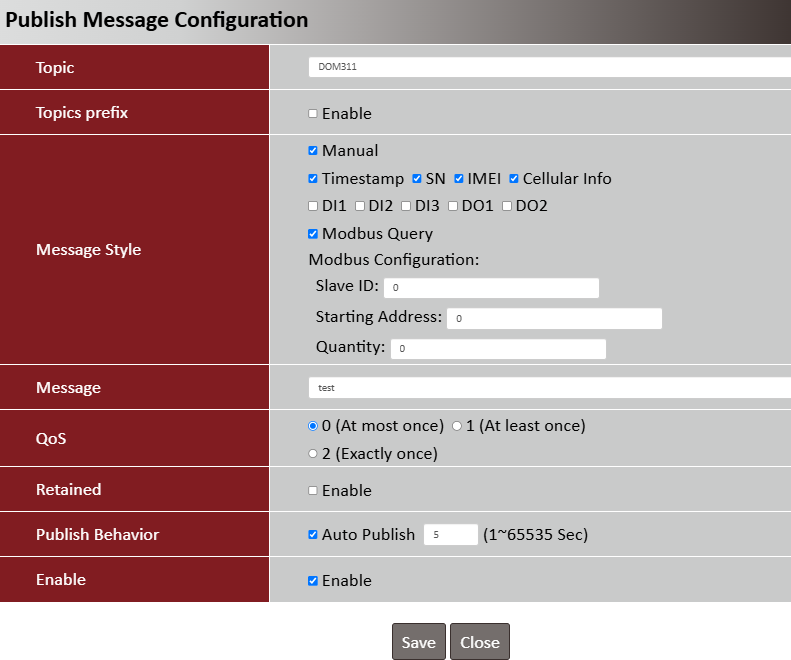
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Topic | Specify the topic for the message to be published |
| Topic prefix | Check the box to add the predefined topic prefix into a MQTT message |
| Message Style | Select a message style from the drop-down list |
| Message |
Specify the message content for the Manual publish message Value Range: 1 ~ 256 characters |
| QoS |
0 (At most once): the message will be published only once, and the broker and subscribed client(s) take no additional steps to acknowledge the delivery, no matter if it is received or not |
| Retained | Check the box to activate this message retaining function |
| Publish Behavior | Auto Publish: auto publish a message with specified time interval (1-65535 sec) |
| Enable | Enable |
Test Result
Please configure the IoT sensor according to the above environment, then validate to ensure everything works as expected.
1. Expected Test Results:
Subscriber HIVEMQ subscribes to topic (DOM311), whose messages contain temperature/humidity and 4G related information, and continues to collect topic (DOM311) from the broker.
2. Test Results:
We take DOM-311-TSO, broker MQTTGO, and Subscriber HIVEMQ as examples to conduct the following tests. And, according to DOM-311-TSO publisher, we set the subscribed topic (DOM311) on the HIVEMQ subscriber.
Subscriber HIVEMQ subscribes to a topic (DOM311), which contains temperature/humidity and 4G related information, and continues to collect topic (DOM311) from broker. This is the test result of temperature/humidity and 4G related information collected on the HIVEMQ Subscriber.